Why Is My Dog's Occiput Getting Bigger? 11 Reasons
Why Is My Dog's Occiput Getting Bigger? 11 Reasons
Vet Reviewed

By: Sarah Hodgson
March 5, 2024
- Posted in Dogs
Table of Contents
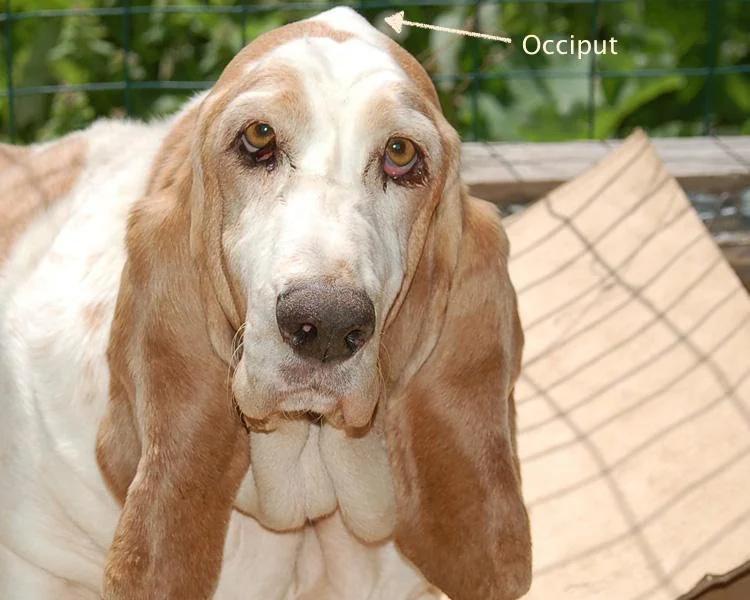
The occiput is the bony protrusion at the back of a dog's head where the skull meets the neck. It's normal for the occiput to be slightly raised and visible in certain breeds, but in some cases, it can become enlarged. There are many reasons why a dog's occiput may be getting bigger. In this article, we'll explore nine of the most common reasons.
Let's dive in!
One possible reason for a dog's occiput getting bigger is normal growth. If the dog is still at an age at which it is growing, the occiput will usually grow in tandem with the rest of the body. Muscle disease is another possible reason for a dog's occiput getting bigger. Certain medical conditions may cause muscle wasting or atrophy, which can lead to a more pronounced occiput.
What Is a Dog's Occiput?
The occiput is a part of the skull located at the back of the head, just above the neck. It is made up of the occipital bone, which is a flat, curved bone that forms the lower rear part of the skull. The occipital bone is connected to the parietal and temporal bones, which form the top and sides of the skull.
Dog skulls come in different shapes, with some breeds having a dolichocephalic (long and narrow) head shape, while others have a brachycephalic (short and wide) head shape. The occiput is an important part of the skull structure, as it provides attachment points for muscles that help to move the head. These muscles are important for a dog's ability to shake their head, turn their head from side to side, and nod.
Occiput Function and Importance
The occiput also plays a vital role in protecting the brain from impact in the event of a fall or collision. This is because the occiput acts as a shock absorber, helping to absorb the force of an impact and reduce the risk of brain injury.
In addition to its protective function, the occiput is also important for sensory perception. The occipital bone contains nerve endings that are responsible for transmitting sensory information from the eyes to the brain. This allows dogs to process visual information and respond to their environment.
Overall, the occiput is an important part of a dog's skull structure, providing both physical protection and sensory perception. Understanding the anatomy and function of the occiput can help dog owners to better understand their pet's health and behavior, and to identify potential issues such as an enlarged occiput or other skull abnormalities.
Common Growth-Related Changes
As dogs grow from puppies to adulthood, their bodies undergo various changes, including changes in the size and shape of their heads. The occiput, which is the bony prominence at the back of the skull, may appear to be getting bigger in some dogs as they grow.
1. Puppy to Adulthood
During the puppy stage, the occiput may be relatively small compared to the rest of the skull. However, as the dog grows and reaches adulthood, the occiput may grow in size along with the rest of the skull. This is a normal growth-related change and is not usually a cause for concern.
2. Breed-Specific Growth Patterns
Different dog breeds have different growth patterns, and some breeds may have larger occiputs than others. For example, breeds such as the Golden Retriever, Basset Hound, German Shepherd, Bloodhound, and Labrador Retriever may have larger occiputs compared to breeds like the Cocker Spaniel, Collie, English Setter, and Dachshund.
It is important to note that the size of the occiput alone does not necessarily indicate a health problem. However, if the occiput is growing at a rapid rate or is accompanied by other symptoms such as pain, discomfort, or neurological issues, it is important to consult a veterinarian to rule out any potential health concerns.
Medical Conditions Affecting the Occiput
If a dog's occiput is getting bigger, it could be due to various medical conditions. In this section, we will discuss some of the common medical conditions that can affect the occiput.
3. Inflammation and Infection
Inflammation and infection can cause swelling and bumps on a dog's occiput. Some of the common causes of inflammation and infection include bacterial and fungal infections, as well as autoimmune diseases. Inflammation and infection can cause muscle atrophy and loss of muscle mass, leading to a swollen occiput. If a dog is showing symptoms of inflammation or infection, it is important to seek veterinary care. A veterinarian can diagnose the underlying cause of the inflammation or infection and provide appropriate treatment.
4. Masticatory Muscle Myositis (MMM)
Masticatory Muscle Myositis (MMM) is a medical condition that affects the muscles in a dog's jaw. The condition can also affect the muscles in the occiput, leading to a swollen occiput. MMM is an autoimmune disease that causes the immune system to attack the dog's own muscle tissue. The condition is more common in certain breeds, such as Golden Retrievers, Doberman Pinschers, and German Shepherds. Symptoms of MMM include difficulty opening the mouth, pain in the jaw, and muscle atrophy. A veterinarian can diagnose MMM through blood work and a physical examination. Treatment for MMM typically involves immunosuppressive medication.
5. Tumors and Cancer
Tumors and cancer can also cause a dog's occiput to get bigger. Tumors can be benign or malignant and can grow anywhere on a dog's body, including the occiput. Symptoms of tumors and cancer can include swelling, bumps, and changes in the size or shape of the occiput. If a dog is showing symptoms of tumors or cancer, it is important to seek veterinary consultation. A veterinarian can diagnose the underlying cause of the symptoms and provide appropriate treatment, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
Physical Factors Contributing to Occiput Size

The size of a dog's occiput can be influenced by a variety of physical factors. These factors range from injury and trauma to muscle development and atrophy. Understanding these factors can help dog owners identify the cause of their dog's enlarged occiput and seek appropriate veterinary care.
6. Injury and Trauma
Injury and trauma to the head and neck can cause swelling and enlargement of the occiput. This can be the result of a head injury, concussion, or other trauma. If a dog has recently experienced a head injury or trauma, it is important to seek veterinary care to determine the extent of the injury and ensure that the dog is comfortable and receiving appropriate care.
7. Muscle Development and Atrophy
Muscle development and atrophy can also contribute to the size of a dog's occiput. If a dog has experienced muscle atrophy in the head and neck area, the occiput may appear larger in comparison. On the other hand, if a dog has experienced significant muscle development in the head and neck area, the occiput may appear smaller in comparison.
Genetic and Breed Influences
When it comes to the size of a dog's occiput, genetic and breed influences play a significant role. Here are some factors to consider:
8. Hereditary Traits
Just like humans, dogs inherit certain physical traits from their parents. Some breeds are more likely to have a larger occiput due to their genetic makeup. For example, dolichocephalic breeds like the English Pointer and Doberman Pinscher tend to have longer, narrower skulls, which can result in a more prominent occiput.
9. Breed-Specific Skull Structures
In addition to overall skull shape, some dog breeds have specific skull structures that can contribute to a larger occiput. For example, Bloodhounds and Basset Hounds have a sagittal crest, a bony ridge that runs along the top of the skull. This can make their occiput appear more pronounced.
On the other hand, brachycephalic breeds like the Bulldog and Pug have a shorter, wider skull shape. This can result in a less prominent occiput.
Note
It's important to note that while breed can be a factor, not all dogs of a particular breed will have the same occiput size. Genetic disposition and individual variation can also play a role.
Behavioral and Environmental Factors
10. Interaction with Predators and Environment
Dogs that spend a lot of time outdoors, especially in areas with predators, may develop a larger occiput as a result of natural selection. The occiput, also referred to as the "smart bump," is believed to be associated with intelligence and knowledge. Dogs that have a larger occiput may have a better sense of their environment and be better equipped to avoid predators. This is because the occiput provides attachment points for muscles that help to move the head. These muscles are important for a dog's ability to shake their head, turn their head from side to side, and nod. Second, it helps to protect the brain from impact in the event of a fall or collision. This is because the occiput acts as a shock absorber.
11. Diet and Nutrition
Diet and nutrition can also play a role in the development of a larger occiput in dogs. A dog that is not receiving adequate nutrition may experience hair loss, which can result in a seemingly enlarged occiput. Additionally, endocrine conditions can cause hair loss in dogs, which can also lead to a larger occiput. It is important to ensure that your dog is receiving a balanced and nutritious diet to prevent any potential health issues.
Assessment and Diagnosis
If a dog owner notices that their dog's occiput is getting bigger, they should consult with a veterinarian for a thorough examination. A veterinarian will perform a physical examination to determine if there are any underlying medical conditions that may be causing the enlargement. During the examination, the veterinarian will palpate the dog's head and neck to feel for any abnormalities or swelling. They will also assess the dog's overall health and look for other symptoms that may be present.
Diagnostic Tests
If the veterinarian suspects an underlying medical condition, they may recommend diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis. Blood work may be ordered to check for any abnormalities in the dog's blood chemistry or to rule out certain conditions. In some cases, a veterinary consultation may be necessary to obtain a more specialized diagnosis.
It is important to note that the enlargement of a dog's occiput may be a normal part of growth and development, especially in younger dogs. However, if the occiput continues to grow or if other symptoms are present, it is important to seek veterinary care to determine the underlying cause.

How Will a Vet Treat It
When a dog's occiput is getting bigger, it is important to seek veterinary care to determine the underlying medical condition causing the enlargement. Treatment options will depend on the specific diagnosis. For example, if the cause is masticatory muscle myositis (MMM), an inflammatory disease that affects the muscles of the face and head used in chewing food, the dog may require immunosuppressive therapy to manage the condition.
In some cases, hormonal imbalances may be the cause of the occiput enlargement. In such cases, hormone replacement therapy may be necessary to correct the imbalance and help manage the condition. It is important to follow the veterinarian's instructions for administering any medications and to monitor the dog's response to treatment closely.
Supportive Care and Prevention
In addition to medical interventions, supportive care can also help manage a dog's occiput enlargement. Providing comfort measures such as soft bedding and avoiding activities that may exacerbate the condition can help the dog feel more comfortable. If the dog is experiencing pain or discomfort, pain management medications may be necessary to help manage the symptoms.
Prevention of occiput enlargement may be possible in some cases. Ensuring that the dog receives adequate nutrition and regular veterinary care can help prevent some underlying medical conditions that may lead to occiput enlargement. Additionally, avoiding activities that may cause head trauma or injury can help prevent occiput enlargement due to impact injuries.
The Bottom Line
So there you have it, the occiput is the bony protrusion at the back of a dog's head where the skull meets the neck. Normal growth, muscle disease, and certain medical conditions are common reasons why a dog's occiput may be getting bigger. If you notice your dog's occiput is getting bigger, it's important to have them evaluated by a veterinarian to determine the underlying cause.
Saftey is always number one!

Subscribe to Petfluence!
Get updates on the latest posts and more from Petfluence straight to your inbox.